vscode配置python调试(debug)
vscode作为宇宙级编辑器,已经越来越多人开始使用它。而它的扩展也琳琅满目,在这里我们介绍下vscode下如何进行python开发和调试。
-
首先,我们需要安装python扩展,打开编辑器,输入ctrl+p,然后输入命令ext install打开扩展搜索。
-
在扩展里面搜素python扩展,然后安装。
-
创建一个文件夹,然后使用vscode打开这个文件夹
-
创建一个文件,然后命名为index.py。
-
配置调试文件,创建launch.json文件。文件内容如下:
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Python",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,//是否在第一条语句时程序停止,下面的这个选项都一样
"pythonPath": "D:\\Program Files (x86)\\Python37-32\\python.exe",//可执行文件路径
"program": "${file}",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput"
]
},
{
"name": "PySpark",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": true,
"osx": {
"pythonPath": "${env:SPARK_HOME}/bin/spark-submit"
},
"windows": {
"pythonPath": "${env:SPARK_HOME}/bin/spark-submit.cmd"
},
"linux": {
"pythonPath": "${env:SPARK_HOME}/bin/spark-submit"
},
"program": "${file}",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput"
]
},
{
"name": "Python Module",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"module": "module.name",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput"
]
},
{
"name": "Integrated Terminal/Console",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"program": "${file}",
"cwd": "",
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit"
]
},
{
"name": "External Terminal/Console",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"program": "${file}",
"cwd": "",
"console": "externalTerminal",
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit"
]
},
{
"name": "Django",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/manage.py",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"args": [
"runserver",
"--noreload",
"--nothreading"
],
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput",
"DjangoDebugging"
]
},
{
"name": "Flask",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"program": "fully qualified path fo 'flask' executable. Generally located along with python interpreter",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"env": {
"FLASK_APP": "${workspaceRoot}/quickstart/app.py"
},
"args": [
"run",
"--no-debugger",
"--no-reload"
],
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput"
]
},
{
"name": "Flask (old)",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": false,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/run.py",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"args": [],
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput"
]
},
{
"name": "Pyramid",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": true,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"args": [
"${workspaceRoot}/development.ini"
],
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput",
"Pyramid"
]
},
{
"name": "Watson",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"stopOnEntry": true,
"pythonPath": "${config:python.pythonPath}",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/console.py",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"args": [
"dev",
"runserver",
"--noreload=True"
],
"env": {},
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.env",
"debugOptions": [
"WaitOnAbnormalExit",
"WaitOnNormalExit",
"RedirectOutput"
]
},
{
"name": "Attach (Remote Debug)",
"type": "python",
"request": "attach",
"localRoot": "${workspaceRoot}",
"remoteRoot": "${workspaceRoot}",
"port": 3000,
"secret": "my_secret",
"host": "localhost"
}
]
}
6.配置任务文件tasks.json.内容如下:
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"taskName": "echo",
"type": "shell",
"command": "D:\\Program Files (x86)\\Python37-32\\python.exe",//Python可执行文件路径
"args": ["${file}"]
}
]
}
7.设置断点,启动调试
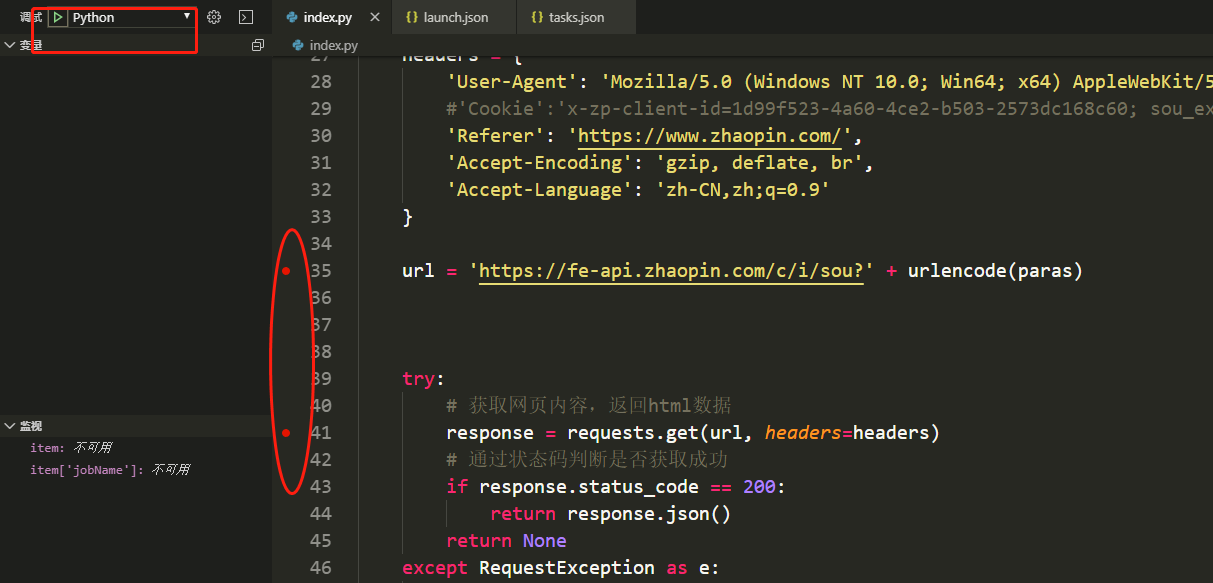
经过上面的步骤,我们就可以变量框中看到本地变量,还可添加监视变量。
launch.json是调试的核心,各个语言都需要这个文件来进行调试,实际上是通过这个文件来调用语言自带的调试工具来调试。



